The history of industrial revolutions
Used for the first time 1837, the expression “industrial revolution” refers to the set of phenomena, which, from the XVIIIᵉ century, have made the world more modern, especially through the development in the West of capitalism, communication tools and production techniques. Today, we can distinguish 4 different industrial revolutions, all bringing a major change:
The first industrial revolution: Mechanical production
This began at the end of the XVIIIᵉ century with the exploitation of coal, the invention of the steam engine and the birth of new industries, such as the textile industry. This marked the appearance of mechanization, which would replace the craft industry. The steam engine will be used to drive the machines and allow increased production rates. All this will allow to have a more important manufacturing and will give birth to products in small series.

The second industrial revolution: Mass production
This second revolution appeared at the end of the XIXᵉ century. This one is based on the use of new energy sources, such as electricity, gas or even oil, whose use is notably linked to the internal combustion engine. It is the time of the big factories and the division of labor. In these factories, we see the appearance of Taylorism and assembly line work, which will make unskilled workers more productive, but which will also raise questions about the meaning of work.
The third industrial revolution: automation of production
This 3ᵉ industrial revolution appeared in the 1970s, with the development of nuclear energy and the arrival of computers in our daily lives. It was also the beginning of robotics, large-scale production and the flexibility of production tools thanks to the implementation of significant automation, which would relieve operators on certain activities.

The 4th industrial revolution: industry 4.0 or the digitalization of information
As for the 4ᵉ industrial revolution, it has appeared during the last few years. It comes from the digitization of various connected devices. This one brings its share of progress and change such as nanotechnology, 3D printing, autonomous cars, all of which can be managed via increasingly autonomous artificial intelligences. Despite the many advances observed, we can still say that we are at the beginning of Industry 4.0. This new industrial revolution is aimed at all industrial companies, of all sectors and all sizes. The objective for these companies is to take a necessary turn for their future by modifying in particular the management of the production mode, by using the new digital tools. This will allow them to adapt to these new modes of consumption which will require to be able to produce personalized products in limited series, the whole without generating additional costs.
An industrial revolution driven by several technologies
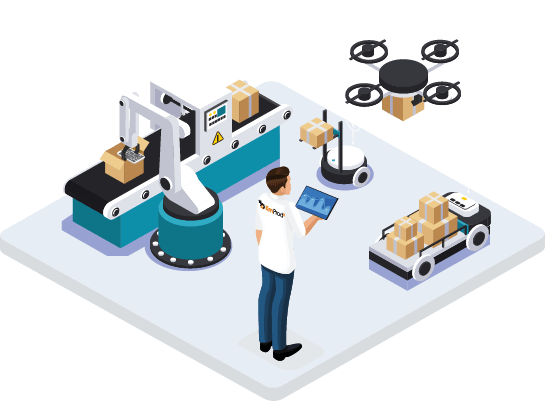
The Cobot
The Cobot or Collaborative Robot allows to revolutionize the industrial world. It is both less dangerous and less expensive for factories.
What is it used for? The Cobot will work alongside the operators and will be able to replace the human arms. It is designed to be the operator’s assistant and to collaborate with him. Easy to program, the collaborative robot will be able to perform different tasks depending on its extensions (grippers, force sensor…).
Cloud computing
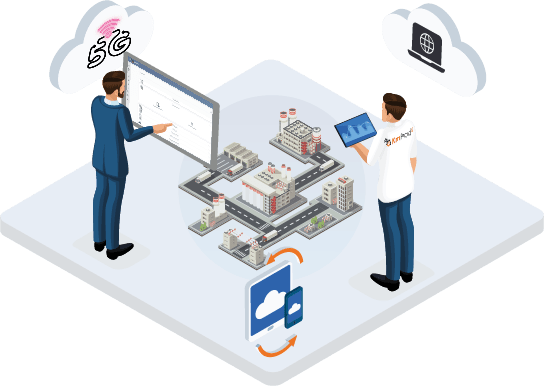
Cloud computing is the access to IT services such as servers, storage, networking… via the Internet. It is one of the essential elements for any Industry 4.0 strategy. The cloud will enable connectivity of production, sales, engineering, supply chain, distribution and services. The cloud will give you the opportunity to process stored and analyzed data more efficiently and cost-effectively.
IoT (Internet of Objects)
The IoT will refer to the network of physical terminals, objects including sensors, software, allowing to connect to other terminals in order to collect, analyze and exchange data between them. It is one of the most decisive elements of smart factories.
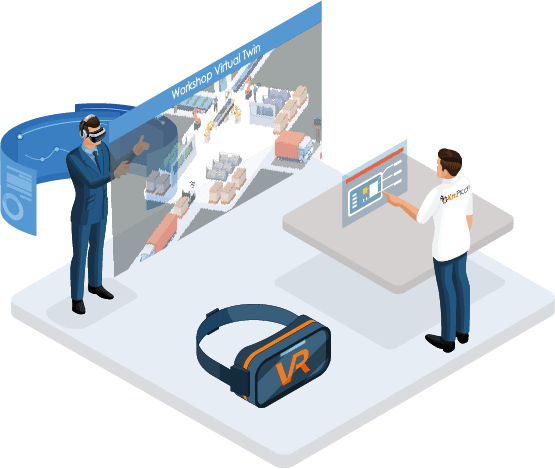
Virtual reality
Virtual reality is used to add virtual elements in our field of vision thanks to an augmented reality headset. What is its contribution to the industry? It is mainly used to rediscover industrial jobs by simplifying and automating certain tasks in order to improve the productivity of the company. The advantages of virtual reality are numerous, here are the main ones
– Accessibility of data in real time
– Reduction of the error rate
– Reduction of production downtime
– Better productivity
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence allows manufacturers to create relevant and scalable information, within the framework of multiple operational processes. This will allow, for example, to perform preventive maintenance thanks to the Artificial Intelligence algorithm having the capacity of automatic learning, which will make it more and more efficient.
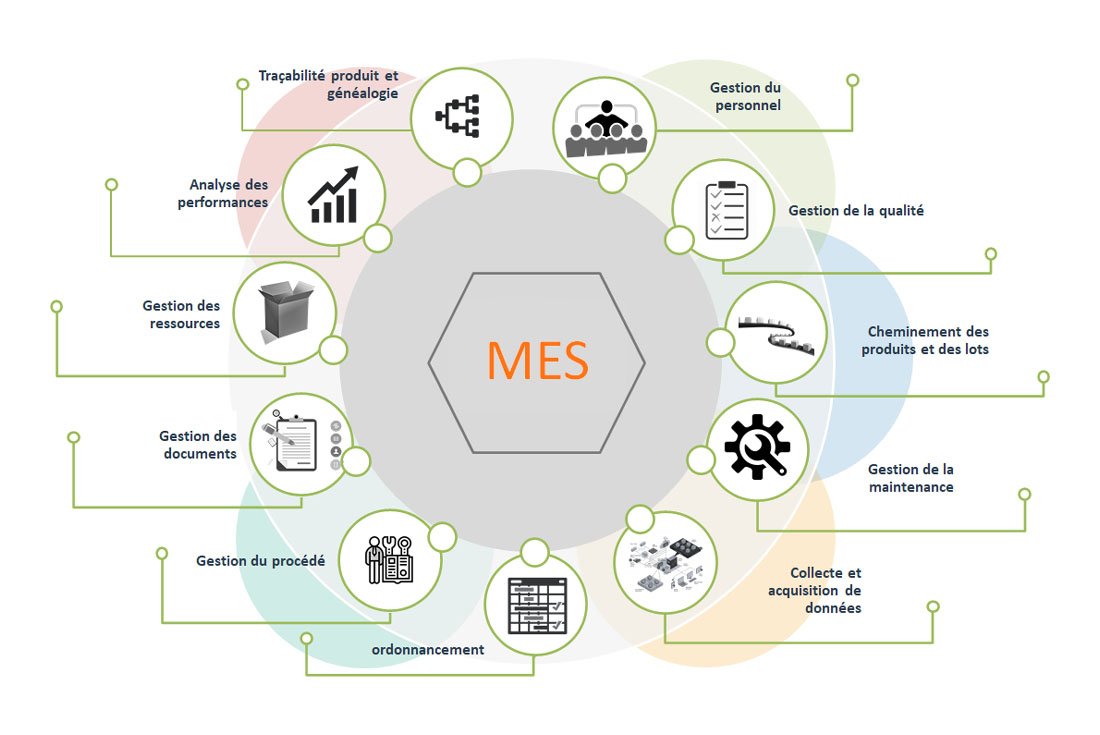
MES, the first essential step in Industry 4.0
What is an MES?
The MES (Manufacturing Execution System) is a concept invented in the 80s. In full expansion especially since the 1990s, it has evolved over the decades and has taken an important place in the Industry 4.0 process. The main objective of an MES is the optimization of activities, from the creation of the manufacturing order to the finished product, the improvement of the production yield.
MES is a production management software, a computer system that, by collecting real-time production data from a factory or shop floor, is able to connect, monitor and control complex manufacturing systems and data flows on the shop floor for better productivity and performance.
The ANSI/ISA-95 standard defines and designates the 11 core functions, 11 domains of MES:
To go further, discover our article: What is an MES software?
MES, the cement of your efficiency
The MES software will allow you to centralize the data present in your workshops and make them communicate with each other. This is only the first step, but it is essential, because it allows you to prepare for future technologies. MES will also be used to fill in gaps in efficiency and “common sense”.
You already have solutions in place (e.g. ERP)? Don’t worry, MES will complement these established software and processes and will make the whole more efficient and connected.

Concrete example:
A company assembling mechanical parts for the aviation industry has to perform quality controls in its production. What is imposed in their specifications is the tightening torque of the screws and nuts by the operators. The company therefore decided to invest in connected metrology tools (Iot).
This data did not communicate with the company’s ERP and was therefore printed. The transit of the information was therefore done by paper before being re-entered later by an operator. The company then noticed problems with wasted time, money and an increased risk of error.
The MES allowed this company to automate this step by going paperless, and to link existing technologies without having to make major structural changes to the company and to have a quick ROI (Return On Investment).
MES allows a faster and cheaper return on investment than robotization or automation, which often comes too early in the modernization of workshops and plants.
It is often more prudent and affordable to start by deploying an MES that will optimize the existing and prepare the ground for the deployment of more modern production devices. The MES acts as a centralizer of all the technologies present on the shop floor, it is the digital heart of the factory.
The most obvious example is the purchase of an automated and robotized line, with data in paper format at each stage of production that will be entered sometimes several times. This will make this purchase less profitable. Especially since the risk of error at each human input is high. Thus, opting for an MES, allowing to manage these various problems and then acquiring automation is generally a better choice for companies.
The MES will allow to centralize and compare the data emitted by all the other technologies present in the workshop. It is the foundation of digitalization.
How to choose your MES according to its state of transition to Industry 4.0?
Monitoring the MES software market is an important point to choose the most adapted solution according to the state of transition to Industry 4.0. An equally crucial element is to know your transition state. For that, the advice and the passage can be sometimes necessary to establish the specifications of your needs. META 2i, can also intervene in this pre-stage via a consulting service that helps you to develop a precise and realistic specification.
What are the different steps to choose the “right” MES software?
Step 1: Choose a proven MES:
There are several points to consider when choosing the MES software that best suits your needs. To do this, you should start by seeing if the chosen solutions have already worked on a project, with similar machines and automats. This way you will have a real point of support to prove the benefit of the MES software in question.
Step 2: choose an MES adapted to our needs and our business.
META 2i realizes 50% of customization on its projects. If, for example, you have a scheduling system in place that works well, we will not replace it without reason. We will be able to fill in the gaps (nothing will replace what is already working if not what will work even better).
A customized MES also allows us to avoid rushing the operators and to accompany the change smoothly while remaining efficient. It allows to be accompanied by a team with experience on similar and varied projects that will be able to give the right answers to the specific needs of each structure.
Step 3: Address the issues one by one.
The entry point of an MES project must be a problem.
Example: a company is not able to answer its quality management problems. The META 2i team will stay by your side on this issue until it is resolved. Then we can move on to the next step.
Deploying an MES is not about solving all the problems at once. Production must continue and never stop in order not to impact the company’s productivity in a negative way.
KmProd is a complete MES software that already answers all these problems. From small workshops to large factories. KmProd was created in the workshops of our historical customers nearly 30 years ago and has evolved with their technologies and problems. It is a software that knows how to answer the daily problems of the industrialists, because it was conceived by and for them. It is the result of a large number of projects carried out in 30 years and in multiple sectors of activity, thanks to which the operational excellence of KmProd has been proven.
Thus, KmProd’s adaptability will be the key to your success in your transition to Industry 4.0.